- жөҸи§Ҳ: 1026498 ж¬Ў
-

ж–Үз« еҲҶзұ»
зӨҫеҢәзүҲеқ—
- жҲ‘зҡ„иө„и®Ҝ ( 0)
- жҲ‘зҡ„и®әеқӣ ( 0)
- жҲ‘зҡ„й—®зӯ” ( 0)
еӯҳжЎЈеҲҶзұ»
- 2012-08 ( 191)
- 2012-07 ( 187)
- 2012-06 ( 102)
- жӣҙеӨҡеӯҳжЎЈ...
жңҖж–°иҜ„и®ә
-
libufengiamпјҡ
еҫҲеҘҪеҫҲејәеӨ§пјҢжҠҘй”ҷдёҚиғҪз”ЁгҖӮ
network: Android зҪ‘з»ңеҲӨж–ӯпјҲwifiгҖҒ3GдёҺе…¶д»–пјү -
kome2000пјҡ
В иҝҷд»Јз Ғ жІЎж•ҲзҺҮе•ҠпјҒеҲ°жҳҜиғҪз”ЁпјҒo(пё¶пёҝпё¶)o е”ү
дҪҝз”ЁMatrixеҜ№bitmapзҡ„ж—ӢиҪ¬е’Ңй•ңеғҸж°ҙе№іеһӮзӣҙзҝ»иҪ¬ -
javadevelopedпјҡ
В В В В В
гҖҠExt JSжқғеЁҒжҢҮеҚ—гҖӢдёҖд№Ұзҡ„жәҗд»Јз ҒдёӢиҪҪең°еқҖ -
javadevelopedпјҡ
В В В В
гҖҠExt JSжқғеЁҒжҢҮеҚ—гҖӢдёҖд№Ұзҡ„жәҗд»Јз ҒдёӢиҪҪең°еқҖ -
javadevelopedпјҡ
[color=red]е°ұејҖдәҶ[/color]
гҖҠExt JSжқғеЁҒжҢҮеҚ—гҖӢдёҖд№Ұзҡ„жәҗд»Јз ҒдёӢиҪҪең°еқҖ
Android_Service 笔记пјҲйҷҶз»ӯжӣҙж–°пјү
Android Serviceи§Јжһҗ иҪ¬http://zy77612.iteye.com/blog/1292649
д»Җд№ҲжҳҜServiceпјҹ
и§Јжғ‘пјҡ
1гҖҒ ServiceдёҚжҳҜеҲҶзҰ»ејҖзҡ„иҝӣзЁӢпјҢйҷӨйқһе…¶д»–зү№ж®Ҡжғ…еҶөпјҢе®ғдёҚдјҡиҝҗиЎҢеңЁиҮӘе·ұзҡ„иҝӣзЁӢпјҢиҖҢжҳҜдҪңдёәеҗҜеҠЁиҝҗиЎҢе®ғзҡ„иҝӣзЁӢзҡ„дёҖйғЁеҲҶгҖӮ
2гҖҒ ServiceдёҚжҳҜзәҝзЁӢпјҢиҝҷж„Ҹе‘ізқҖе®ғе°ҶеңЁдё»зәҝзЁӢйҮҢеҠідҪңгҖӮ
еҗҜеҠЁserviceжңүдёӨз§Қж–№жі•пјҡ
1гҖҒ Context.startService()
и°ғз”ЁиҖ…дёҺжңҚеҠЎд№Ӣй—ҙжІЎжңүе…іиҒ”пјҢеҚідҪҝи°ғз”ЁиҖ…йҖҖеҮәпјҢжңҚеҠЎд»ҚеҸҜиҝҗиЎҢ
2гҖҒ Context.bindService()
и°ғз”ЁиҖ…дёҺжңҚеҠЎз»‘е®ҡеңЁдёҖиө·пјҢи°ғз”ЁиҖ…дёҖж—ҰйҖҖеҮәпјҢжңҚеҠЎд№ҹе°ұз»Ҳжӯў
Serviceзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹ
еҰӮжһңдҪҝз”ЁstartService()еҗҜеҠЁserviceпјҢзі»з»ҹе°ҶйҖҡиҝҮдј е…Ҙзҡ„IntentеңЁеә•еұӮжҗңзҙўзӣёе…із¬ҰеҗҲIntentйҮҢйқўдҝЎжҒҜзҡ„serviceгҖӮеҰӮжһңжңҚеҠЎжІЎжңүеҗҜеҠЁеҲҷе…ҲиҝҗиЎҢonCreateпјҢ然еҗҺиҝҗиЎҢonStartCommand пјҲеҸҜеңЁйҮҢйқўеӨ„зҗҶеҗҜеҠЁж—¶дј иҝҮжқҘзҡ„Intentе’Ңе…¶д»–еҸӮж•°пјүпјҢзӣҙеҲ°жҳҺжҳҫи°ғз”ЁstopServiceжҲ–иҖ…stopSelfжүҚе°ҶеҒңжӯўServiceгҖӮж— и®әиҝҗиЎҢstartServiceеӨҡе°‘ж¬ЎпјҢеҸӘиҰҒи°ғз”ЁдёҖж¬ЎstopServiceжҲ–иҖ…stopSelfпјҢServiceйғҪдјҡеҒңжӯўгҖӮдҪҝз”ЁstopSelf(int)ж–№жі•еҸҜд»ҘдҝқиҜҒеңЁеӨ„зҗҶеҘҪintentеҗҺеҶҚеҒңжӯўгҖӮ
жҺ§еҲ¶serviceиҝҗиЎҢзҡ„дё»иҰҒж–№ејҸжңүдёӨз§ҚпјҢдё»иҰҒжҳҜж №жҚ®onStartCommandж–№жі•иҝ”еӣһзҡ„ж•°еҖјгҖӮж–№жі•пјҡ
1гҖҒSTART_STICKY
2гҖҒSTART_NOT_STICKYorSTART_REDELIVER_INTENT
иҝҷйҮҢдё»иҰҒи§ЈйҮҠиҝҷдёүдёӘеҸҳйҮҸзҡ„ж„Ҹд№үпјҡ
1гҖҒ START_STICKY
еңЁиҝҗиЎҢonStartCommandеҗҺserviceиҝӣзЁӢиў«killеҗҺпјҢйӮЈе°Ҷдҝқз•ҷеңЁејҖе§ӢзҠ¶жҖҒпјҢдҪҶжҳҜдёҚдҝқз•ҷйӮЈдәӣдј е…Ҙзҡ„intentгҖӮдёҚд№…еҗҺserviceе°ұдјҡеҶҚж¬Ўе°қиҜ•йҮҚж–°еҲӣе»әпјҢеӣ дёәдҝқз•ҷеңЁејҖе§ӢзҠ¶жҖҒпјҢеңЁеҲӣе»ә serviceеҗҺе°ҶдҝқиҜҒи°ғз”ЁonstartCommandгҖӮеҰӮжһңжІЎжңүдј йҖ’д»»дҪ•ејҖе§Ӣе‘Ҫд»Өз»ҷserviceпјҢйӮЈе°ҶиҺ·еҸ–еҲ°nullзҡ„intent
2гҖҒ START_NOT_STICKY
еңЁиҝҗиЎҢonStartCommandеҗҺserviceиҝӣзЁӢиў«killеҗҺпјҢ并且没жңүж–°зҡ„intentдј йҖ’з»ҷе®ғгҖӮServiceе°Ҷ移еҮәејҖе§ӢзҠ¶жҖҒпјҢ并且зӣҙеҲ°ж–°зҡ„жҳҺжҳҫзҡ„ж–№жі•пјҲstartServiceпјүи°ғз”ЁжүҚйҮҚж–°еҲӣе»әгҖӮеӣ дёәеҰӮжһңжІЎжңүдј йҖ’д»»дҪ•жңӘеҶіе®ҡзҡ„intentйӮЈд№ҲserviceжҳҜдёҚдјҡеҗҜеҠЁпјҢд№ҹе°ұжҳҜжңҹй—ҙonstartCommandдёҚдјҡжҺҘ收еҲ°д»»дҪ•nullзҡ„intentгҖӮ
3гҖҒ START_REDELIVER_INTENT
еңЁиҝҗиЎҢonStartCommandеҗҺserviceиҝӣзЁӢиў«killеҗҺпјҢзі»з»ҹе°ҶдјҡеҶҚж¬ЎеҗҜеҠЁserviceпјҢе№¶дј е…ҘжңҖеҗҺдёҖдёӘintentз»ҷonstartCommandгҖӮзӣҙеҲ°и°ғз”ЁstopSelf(int)жүҚеҒңжӯўдј йҖ’intentгҖӮеҰӮжһңеңЁиў«killеҗҺиҝҳжңүжңӘеӨ„зҗҶеҘҪзҡ„intentпјҢйӮЈиў«killеҗҺжңҚеҠЎиҝҳжҳҜдјҡиҮӘеҠЁеҗҜеҠЁгҖӮеӣ жӯӨonstartCommandдёҚдјҡжҺҘ收еҲ°д»»дҪ•nullзҡ„intentгҖӮ
е®ўжҲ·з«Ҝд№ҹеҸҜд»ҘдҪҝз”ЁbindServiceжқҘдҝқжҢҒи·ҹserviceжҢҒд№…е…іиҒ”гҖӮи°Ёи®°пјҡеҰӮжһңдҪҝз”Ёиҝҷз§Қж–№жі•пјҢйӮЈд№Ҳе°ҶдёҚдјҡи°ғз”ЁonstartCommandпјҲи·ҹstartServiceдёҚдёҖж ·пјҢдёӢйқўдҫӢеӯҗжіЁйҮҠд№ҹжңүи§ЈжһҗпјҢеӨ§е®¶еҸҜиҜ•иҜ•пјүгҖӮе®ўжҲ·з«Ҝе°ҶдјҡеңЁonBindеӣһи°ғдёӯжҺҘ收еҲ°IBinderжҺҘеҸЈиҝ”еӣһзҡ„еҜ№иұЎгҖӮйҖҡеёёIBinderдҪңдёәдёҖдёӘеӨҚжқӮзҡ„жҺҘеҸЈйҖҡеёёжҳҜиҝ”еӣһaidlж•°жҚ®гҖӮ
Serviceд№ҹеҸҜд»Ҙж··еҗҲstartе’ҢbindдёҖиө·дҪҝз”ЁгҖӮ
жқғйҷҗ
иҰҒиҝҗиЎҢserviceпјҢйҰ–е…Ҳеҝ…йЎ»еңЁAndroidManifest.xmlйҮҢз”іжҳҺ<service>ж ҮзӯҫгҖӮ
ServiceиғҪеӨҹдҝқжҠӨдёӘдәәзҡ„IPCи°ғз”ЁпјҢжүҖд»ҘеңЁжү§иЎҢе®һзҺ°иҜҘи°ғз”Ёж—¶еүҚе…ҲдҪҝз”ЁcheckCallingPermission(String)ж–№жі•жЈҖжҹҘжҳҜеҗҰжңүиҝҷдёӘжқғйҷҗгҖӮ
иҝӣзЁӢз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹ
еҪ“serviceиҝҗиЎҢеңЁдҪҺеҶ…еӯҳзҡ„зҺҜеўғж—¶пјҢе°ҶдјҡkillжҺүдёҖдёӢеӯҳеңЁзҡ„иҝӣзЁӢгҖӮеӣ жӯӨиҝӣзЁӢзҡ„дјҳе…Ҳзә§е°ҶдјҡеҫҲйҮҚиҰҒпјҡ
1гҖҒ еҰӮжһңserviceеҪ“еүҚжӯЈеңЁжү§иЎҢonCreateгҖҒonStartCommandгҖҒonDestroyж–№жі•пјҢдё»иҝӣзЁӢе°ҶдјҡжҲҗдёәеүҚеҸ°иҝӣзЁӢжқҘдҝқиҜҒд»Јз ҒеҸҜд»Ҙжү§иЎҢе®ҢжҲҗйҒҝе…Қиў«kill
2гҖҒ еҰӮжһңserviceе·Із»ҸеҗҜеҠЁдәҶпјҢйӮЈд№Ҳдё»иҝӣзЁӢе°ҶдјҡжҜ”е…¶д»–еҸҜи§Ғзҡ„иҝӣзЁӢзҡ„йҮҚиҰҒжҖ§дҪҺпјҢдҪҶжҜ”е…¶д»–зңӢдёҚи§Ғзҡ„иҝӣзЁӢй«ҳгҖӮеӣ дёәеҸӘжңүе°‘йғЁеҲҶиҝӣзЁӢе§Ӣз»ҲжҳҜз”ЁжҲ·еҸҜи§Ғзҡ„пјҢеӣ жӯӨйҷӨйқһеңЁжһҒеәҰдҪҺеҶ…еӯҳзҡ„ж—¶еҖҷпјҢдёҚ然 serviceжҳҜдёҚдјҡиў«killзҡ„гҖӮ
3гҖҒ еҰӮжһңжңүе®ўжҲ·з«Ҝе…іиҒ”еҲ°serviceпјҢйӮЈд№Ҳserviceж°ёиҝңжҜ”е®ўжҲ·з«ҜйҮҚиҰҒгҖӮд№ҹе°ұжҳҜиҜҙе®ўжҲ·з«ҜеҸҜи§ҒпјҢйӮЈд№Ҳserviceд№ҹеҸҜи§ҒпјҲжҲ‘зҗҶи§ЈиҝҷйҮҢзҡ„еҸҜи§Ғ并дёҚжҳҜеҸҜд»ҘзңӢеҲ°пјҢиҖҢжҳҜйҮҚиҰҒжҖ§пјҢеӣ дёәеҸҜи§ҒеҫҖеҫҖе°ұиЎЁзӨәйҮҚиҰҒжҖ§й«ҳпјүгҖӮ
4гҖҒ ServiceеҸҜд»ҘдҪҝз”ЁstartForeground APIе°Ҷserviceж”ҫеҲ°еүҚеҸ°зҠ¶жҖҒгҖӮиҝҷж ·еңЁдҪҺеҶ…еӯҳж—¶иў«killзҡ„еҮ зҺҮжӣҙдҪҺпјҢдҪҶжҳҜж–ҮжЎЈеҗҺйқўеҸҲеҶҷдәҶпјҢеҰӮжһңеңЁжһҒеәҰжһҒеәҰдҪҺеҶ…еӯҳзҡ„еҺӢеҠӣдёӢпјҢиҜҘserviceзҗҶи®әдёҠиҝҳжҳҜдјҡиў«killжҺүгҖӮдҪҶиҝҷдёӘжғ…еҶөеҹәжң¬дёҚз”ЁиҖғиҷ‘гҖӮ
еҪ“然еҰӮжһңserviceжҖҺд№ҲдҝқжҢҒиҝҳжҳҜиў«killдәҶпјҢйӮЈдҪ еҸҜд»ҘйҖҡиҝҮйҮҚеҶҷonStartCommandиҝ”еӣһеҸҳйҮҸжқҘи®ҫзҪ®е®ғзҡ„еҗҜеҠЁж–№ејҸгҖӮжҜ”еҰӮпјҡSTART_STICKYгҖҒSTART_REDELIVER_INTENTзӯүзӯүпјҢеүҚйқўе·Із»Ҹи®Ёи®әдәҶе®ғ们зҡ„дҪңз”ЁпјҢиҝҷйҮҢе°ұдёҚеҶҚзҙҜиөҳдәҶ
еҸҰеӨ–пјҡ
service зҡ„onCreateе’ҢonStartCommand жҳҜиҝҗиЎҢеңЁдё»зәҝзЁӢзҡ„пјҢжүҖд»ҘеҰӮжһңйҮҢйқўжңүеӨ„зҗҶиҖ—ж—¶й—ҙзҡ„д»»еҠЎгҖӮдёӨз§ҚеӨ„зҗҶпјҡ
1гҖҒ иҜ·е°Ҷе®ғ们йғҪжҢӘеҲ°ж–°зҡ„зәҝзЁӢйҮҢгҖӮ
2гҖҒ з”Ёзі»з»ҹжҸҗдҫӣзҡ„IntentServiceпјҢе®ғ继жүҝдәҶServiceпјҢе®ғеӨ„зҗҶж•°жҚ®жҳҜз”ЁиҮӘиә«ж–°ејҖзҡ„зәҝзЁӢгҖӮ
еҘҪдәҶиҜҙдәҶиҝҷд№ҲеӨҡдёӢйқўе°ұжҳҜдҫӢеӯҗзҡ„ж—¶еҲ»дәҶгҖӮжҖ»е…ұжңүдёӨдёӘдҫӢеӯҗпјҢ第дёҖдёӘжҳҜжң¬ең°и°ғз”ЁпјҢ第дәҢдёӘжҳҜиҝңзЁӢи°ғз”Ё.
еҸЈж°ҙеҝ«жІЎдәҶпјҢжүҖд»ҘдёӢйқўе°ұзӣҙжҺҘиҝӣе…Ҙд»Јз ҒзҺҜиҠӮеҗ§гҖӮд»Јз ҒйҮҢйқўе·Із»ҸжңүиҜҰз»Ҷзҡ„жіЁи§ЈдәҶпјҢеҰӮжһңзңҹзҡ„зңҹзҡ„иҝҳжҳҜдёҚжҳҺзҷҪпјҢйӮЈе°ұжҳҜжҲ‘иҝҷзҜҮдәҢжүӢйһӢзҡ„еӨұиҙҘдәҶгҖӮ:(
public class LocalService extends Service {
private NotificationManager mNM;
// йҖҡзҹҘе”ҜдёҖж ҮзӨәпјҢеңЁйҖҡзҹҘејҖе§Ӣе’Ңз»“жқҹдҪҝз”Ё
private int NOTIFICATION = R.string.local_service_started;
// дёҺз•ҢйқўдәӨдә’зҡ„зұ»пјҢз”ұдәҺserviceи·ҹз•ҢйқўжҖ»жҳҜиҝҗиЎҢеңЁеҗҢдёҖзЁӢеәҸйҮҢпјҢжүҖд»ҘдёҚз”ЁеӨ„зҗҶIPC
public class LocalBinder extends Binder {
LocalService getService() {
return LocalService.this;
}
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
mNM = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
// еңЁserviceејҖе§Ӣж—¶пјҢе°Ҷiconеӣҫж Үж”ҫеҲ°йҖҡзҹҘд»»еҠЎж Ҹ
showNotification();
}
//
private void showNotification() {
CharSequence text = getText(R.string.local_service_started);
Notification notification = new Notification(R.drawable.icon, text,
System.currentTimeMillis());
// еҪ“зӮ№еҮ»йҖҡзҹҘж—¶пјҢеҗҜеҠЁиҜҘcontentIntentе…іиҒ”зҡ„activity
PendingIntent contentIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0,
new Intent(this, showActivity.class), 0);
// еңЁйҖҡзҹҘж ҸдёҠжҳҫзӨәж Үйўҳе’ҢеҶ…е®№
notification.setLatestEventInfo(this,
getText(R.string.local_service_label), text, contentIntent);
mNM.notify(NOTIFICATION, notification);
}
// е…је®№2.0д»ҘеүҚзүҲжң¬
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
}
// еңЁ2.0д»ҘеҗҺзҡ„зүҲжң¬еҰӮжһңйҮҚеҶҷдәҶonStartCommandпјҢйӮЈonStartе°ҶдёҚдјҡиў«и°ғз”ЁпјҢжіЁпјҡеңЁ2.0д»ҘеүҚжҳҜжІЎжңүonStartCommandж–№жі•
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.i("Service", "Received start id " + startId + ": " + intent);
// еҰӮжһңжңҚеҠЎиҝӣзЁӢеңЁе®ғеҗҜеҠЁеҗҺ(д»ҺonStartCommand()иҝ”еӣһеҗҺ)иў«killжҺү, йӮЈд№Ҳи®©д»–е‘ҶеңЁеҗҜеҠЁзҠ¶жҖҒдҪҶдёҚеҸ–дј з»ҷе®ғзҡ„intent.
// йҡҸеҗҺзі»з»ҹдјҡйҮҚеҶҷеҲӣе»әserviceпјҢеӣ дёәеңЁеҗҜеҠЁж—¶пјҢдјҡеңЁеҲӣе»әж–°зҡ„serviceж—¶дҝқиҜҒиҝҗиЎҢonStartCommand
// еҰӮжһңжІЎжңүд»»дҪ•ејҖе§ӢжҢҮд»ӨеҸ‘йҖҒз»ҷserviceпјҢйӮЈе°Ҷеҫ—еҲ°nullзҡ„intentпјҢеӣ жӯӨеҝ…йЎ»жЈҖжҹҘе®ғ.
// иҜҘж–№ејҸеҸҜз”ЁеңЁејҖе§Ӣе’ҢеңЁиҝҗиЎҢдёӯд»»ж„Ҹж—¶еҲ»еҒңжӯўзҡ„жғ…еҶөпјҢдҫӢеҰӮдёҖдёӘserviceжү§иЎҢйҹід№җеҗҺеҸ°зҡ„йҮҚж”ҫ
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
mNM.cancel(NOTIFICATION);
Toast
.makeText(this, R.string.local_service_stopped,
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
private final IBinder mBinder = new LocalBinder();
}
public class LocalActivity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
private LocalService mBoundService;
private boolean mIsBound;
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// еҪ“иҝӣзЁӢеҙ©жәғж—¶е°Ҷиў«и°ғз”ЁпјҢеӣ дёәиҝҗиЎҢеңЁеҗҢдёҖзЁӢеәҸпјҢеҰӮжһңжҳҜеҙ©жәғе°ҶжүҖд»Ҙж°ёиҝңдёҚдјҡеҸ‘з”ҹ
// еҪ“и§ЈйҷӨз»‘е®ҡж—¶д№ҹиў«и°ғз”Ё
mBoundService = null;
Toast.makeText(LocalActivity.this,
R.string.local_service_disconnected, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// serviceиҝһжҺҘе»әз«Ӣж—¶е°Ҷи°ғз”ЁиҜҘж–№жі•
mBoundService = ((LocalService.LocalBinder) service).getService();
Toast.makeText(LocalActivity.this,
R.string.local_service_connected, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
};
void doBindService() {
// е»әз«ӢserviceиҝһжҺҘгҖӮеӣ дёәжҲ‘们зҹҘйҒ“зЁӢеәҸдјҡиҝҗиЎҢеңЁжң¬ең°йҮҢпјҢеӣ жӯӨдҪҝз”ЁжҳҫзӨәзҡ„зұ»еҗҚжқҘе®һзҺ°service
// пјҲдҪҶжҳҜдёҚж”ҜжҢҒи·ҹе…¶д»–зЁӢеәҸдәӨдә’пјү
// дёӨз§Қдј йҖ’пјҢдёҖз§ҚжҳҜеңЁmanifestйҮҢеҶҷеҘҪintent-filterзҡ„actionпјҢдёҖз§ҚжҳҜжҳҫзӨәдј йҖ’
// bindService(new Intent("com.LocalService.LocalService"), mConnection,
// Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
// bindService(new Intent(LocalActivity.this, LocalService.class),
// mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
//еҰӮжһңз”Ёиҝҷз§Қж–№жі•е°Ҷдјҡи°ғз”ЁonStartCommandж–№жі•
startService(new Intent(LocalActivity.this, LocalService.class));
mIsBound = true;
}
void doUnbindService() {
if (mIsBound) {
// Detach our existing connection.
stopService(new Intent(LocalActivity.this, LocalService.class));
// unbindService(mConnection);
mIsBound = false;
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
doUnbindService();
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
doBindService();
}
}
еӨ§е®¶еҸҜд»ҘиҜ•иҜ•startService е’ҢbindServiceиҝҷдёӨз§ҚеҢәеҲ«гҖӮ
иҪ»жқҫдёҖдёӢпјҢToast.makeText(this, "жё©йҰЁжҸҗзӨәпјҡ\nд»Јз Ғе·Із»ҸеҶҷеҘҪдәҶпјҢеҰӮжһңжғіжөӢиҜ•дёҖдёӢеҸҜд»ҘеҺ»жҺүжіЁйҮҠзҡ„е–”", 2000).show(); ^-^
дёӢйқўжҳҜиҝңзЁӢи°ғз”Ёзҡ„дҫӢеӯҗпјҢдё»иҰҒжҳҜз”Ёзі»з»ҹжҸҗдҫӣзҡ„MessengerпјҢзңҒеҺ»иҮӘе·ұеҺ»еҶҷеӨҚжқӮзҡ„aidlж–Ү件
<service android:name="MessengerService" android:process=":remote">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.LocalService.MessengerService" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
еҰӮжһңеҠ дәҶandroid:process=":remote" пјҢйӮЈеңЁи°ғиҜ•ж—¶еңЁserviceж–ӯзӮ№жҳҜдёҚдјҡи§ҰеҸ‘зҡ„гҖӮ
public class MessengerService extends Service {
private NotificationManager mNM;
// дҝқеӯҳжүҖжңүи·ҹжңҚеҠЎиҝһжҺҘзҡ„е®ўжҲ·з«Ҝ
ArrayList<Messenger> mClients = new ArrayList<Messenger>();
// дҝқеӯҳжңҖеҗҺдёҖж¬Ўи·ҹжңҚеҠЎиҝһжҺҘзҡ„е®ўжҲ·з«Ҝзҡ„ж Үеҝ—
int mValue = 0;
// жіЁеҶҢжҢҮд»ӨпјҢMessage's replyTo еӯ—ж®өеҖјеҝ…йЎ»жҳҜclient зҡ„Messenger
static final int MSG_REGISTER_CLIENT = 1;
// еҸ–ж¶ҲжҢҮд»ӨпјҢMessage's replyTo еӯ—ж®өеҖјеҝ…йЎ»жҳҜе…ҲеүҚзөҰMSG_REGISTER_CLIENTзҡ„Messenger
static final int MSG_UNREGISTER_CLIENT = 2;
// жңҚеҠЎеҸ‘йҖҒжҢҮд»ӨпјҢеҸҜд»ҘеңЁе®ўжҲ·з«Ҝе’ҢжңҚеҠЎзӣҙжҺҘдәӨжөҒ
static final int MSG_SET_VALUE = 3;
// еӨ„зҗҶе®ўжҲ·з«Ҝдј йҖҒиҝҮжқҘзҡ„ж¶ҲжҒҜ
class IncomingHandler extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_REGISTER_CLIENT:
// Optional Messenger where replies to this message can be sent.
// The semantics of exactly how this is used are up to the
// sender and receiver.
mClients.add(msg.replyTo);
break;
case MSG_UNREGISTER_CLIENT:
mClients.remove(msg.replyTo);
break;
case MSG_SET_VALUE:
mValue = msg.arg1;
for (int i = mClients.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
try {
mClients.get(i).send(
Message.obtain(null, MSG_SET_VALUE, mValue, 0));
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// иҝңзЁӢе®ўжҲ·з«ҜеҮәй”ҷпјҢд»Һlistдёӯ移йҷӨ
// йҒҚеҺҶеҲ—иЎЁд»ҘдҝқиҜҒеҶ…йғЁеҫӘзҺҜе®үе…ЁиҝҗиЎҢ
mClients.remove(i);
}
}
break;
default:
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
Log.i("Service", "жңү" + mClients.size() + "е®ўжҲ·з«Ҝ");
}
}
// еҲӣе»әдёҖдёӘж–°зҡ„Messengerи·ҹе·ІеӯҳеңЁзҡ„Handlerе…іиҒ”
// еҰӮжһңжңүд»»дҪ•ж¶ҲжҒҜеҸ‘йҖҒеҲ°MessengerпјҢе°ҶдәӨз»ҷHandlerеӨ„зҗҶ
final Messenger mMessenger = new Messenger(new IncomingHandler());
@Override
public void onCreate() {
mNM = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
// еңЁserviceејҖе§Ӣж—¶пјҢе°Ҷiconеӣҫж Үж”ҫеҲ°йҖҡзҹҘд»»еҠЎж Ҹ
showNotification();
}
//
private void showNotification() {
CharSequence text = getText(R.string.local_service_started);
Notification notification = new Notification(R.drawable.icon, text,
System.currentTimeMillis());
// еҪ“зӮ№еҮ»йҖҡзҹҘж—¶пјҢеҗҜеҠЁиҜҘcontentIntentе…іиҒ”зҡ„activity
PendingIntent contentIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0,
new Intent(this, showActivity.class), 0);
// еңЁйҖҡзҹҘж ҸдёҠжҳҫзӨәж Үйўҳе’ҢеҶ…е®№
notification.setLatestEventInfo(this,
getText(R.string.remote_service_label), text, contentIntent);
mNM.notify(R.string.remote_service_started, notification);
}
//
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.i("Service", "Received start id " + startId + ": " + intent);
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
mNM.cancel(R.string.remote_service_started);
Toast.makeText(this, R.string.remote_service_stopped,
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mMessenger.getBinder();
}
}
public class MessengerActivity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
private Messenger mService = null;
private boolean mIsBound;
private TextView mCallbackText;
class IncomingHandler extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MessengerService.MSG_SET_VALUE:
mCallbackText.setText("Received from service: " + msg.arg1);
break;
default:
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
}
}
final Messenger mMessenger = new Messenger(new IncomingHandler());
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// еҪ“иҝӣзЁӢеҙ©жәғж—¶е°Ҷиў«и°ғз”ЁпјҢеӣ дёәиҝҗиЎҢеңЁеҗҢдёҖзЁӢеәҸпјҢеҰӮжһңжҳҜеҙ©жәғе°ҶжүҖд»Ҙж°ёиҝңдёҚдјҡеҸ‘з”ҹ
// еҪ“и§ЈйҷӨз»‘е®ҡж—¶д№ҹиў«и°ғз”Ё
mService = null;
mCallbackText.setText("Disconnected.");
Toast.makeText(MessengerActivity.this,
R.string.remote_service_disconnected, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// serviceиҝһжҺҘе»әз«Ӣж—¶е°Ҷи°ғз”ЁиҜҘж–№жі•
// иҝ”еӣһIBinderжҺҘеҸЈд»ҘдҫҝжҲ‘们еҸҜд»Ҙи·ҹserviceе…іиҒ”гҖӮ
// жҲ‘们еҸҜйҖҡиҝҮIDLжҺҘеҸЈжқҘдәӨжөҒ
mService = new Messenger(service);
mCallbackText.setText("Attached.");
// еҸӘжңүжҲ‘们иҝһжҺҘзқҖйғҪзӣ‘еҗ¬зқҖжңҚеҠЎ
try {
// жіЁеҶҢ
Message msg = Message.obtain(null,
MessengerService.MSG_REGISTER_CLIENT);
msg.replyTo = mMessenger;
mService.send(msg);
// дҫӢеӯҗ
msg = Message.obtain(null, MessengerService.MSG_SET_VALUE,
11111111, 0);
mService.send(msg);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// In this case the service has crashed before we could even
// do anything with it; we can count on soon being
// disconnected (and then reconnected if it can be restarted)
// so there is no need to do anything here.
}
Toast.makeText(MessengerActivity.this,
R.string.remote_service_connected, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
};
void doBindService() {
bindService(new Intent(MessengerActivity.this, MessengerService.class),
mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
mIsBound = true;
mCallbackText.setText("Binding.");
}
void doUnbindService() {
if (mIsBound) {
if (mService != null) {
try {
// еҸ–ж¶ҲжіЁеҶҢ
Message msg = Message.obtain(null,
MessengerService.MSG_UNREGISTER_CLIENT);
msg.replyTo = mMessenger;
mService.send(msg);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// There is nothing special we need to do if the service
// has crashed.
}
}
// Detach our existing connection.
unbindService(mConnection);
mIsBound = false;
mCallbackText.setText("Unbinding.");
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
doUnbindService();
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.messenger);
mCallbackText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text);
doBindService();
}
}
жөӢиҜ•иҝңзЁӢи°ғз”ЁпјҢжҲ‘еј„еӨҡдёҖд»ҪйЎ№зӣ®жқҘжөӢиҜ•пјҢдё»иҰҒжҳҜжҹҘзңӢжҳҜеҗҰиҝһжҺҘжҲҗеҠҹе’ҢжңүеӨҡе°‘дёӘе®ўжҲ·з«ҜиҝһжҺҘдёҠ.
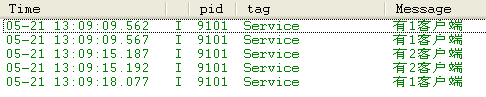
- 2012-02-01 22:18
- жөҸи§Ҳ 807
- иҜ„и®ә(0)
- жҹҘзңӢжӣҙеӨҡ





зӣёе…іжҺЁиҚҗ
Android_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®° Android_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®° Android_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°
Android_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°
axisејҖеҸ‘web_serviceзЁӢеәҸ_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°,еӯҰд№ axisејҖеҸ‘пјҢеӯҰд№ з¬”и®°
Androidеә”з”ЁејҖеҸ‘_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°.docAndroidеә”з”ЁејҖеҸ‘_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°.docAndroidеә”з”ЁејҖеҸ‘_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°.docAndroidеә”з”ЁејҖеҸ‘_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°.doc
Spring_AOP笔记Spring_AOP笔记Spring_AOP笔记Spring_AOP笔记Spring_AOP笔记Spring_AOP笔记Spring_AOP笔记
android_fragmentеӯҰд№ з¬”и®°.pdf
иҖ¶йІҒеҚҡејҲи®ә24и®І_全笔记_v_2.1
MongoDB_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°MongoDB_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°MongoDB_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°MongoDB_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°MongoDB_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°MongoDB_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°MongoDB_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°MongoDB_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°MongoDB_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°MongoDB_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°MongoDB_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°MongoDB_еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°MongoDB_...
ең°зҗҶдҝЎжҒҜзі»з»ҹжҰӮи®ә_иҜ»д№Ұ笔记_й»„жқҸе…ғ_ең°зҗҶдҝЎжҒҜзі»з»ҹжҰӮи®ә_иҜ»д№Ұ笔记_й»„жқҸе…ғ_ең°зҗҶдҝЎжҒҜзі»з»ҹжҰӮи®ә_иҜ»д№Ұ笔记_й»„жқҸе…ғ_ең°зҗҶдҝЎжҒҜзі»з»ҹжҰӮи®ә_иҜ»д№Ұ笔记_й»„жқҸе…ғ_ең°зҗҶдҝЎжҒҜзі»з»ҹжҰӮи®ә_иҜ»д№Ұ笔记_й»„жқҸе…ғ_ең°зҗҶдҝЎжҒҜзі»з»ҹжҰӮи®ә_иҜ»д№Ұ笔记_й»„жқҸе…ғ_
Android_ NDKзј–зЁӢе…Ҙ门笔记
EGLжҳҜOpenGL ESдёҺжң¬ең°Windowзі»з»ҹд№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„жЎҘжўҒгҖӮEGLеҲӣе»әжёІжҹ“дёҠдёӢж–ҮпјҲRendering Contextпјүе’ҢSurfaceпјҢRendering ContextжҳҜOpenGL ESзҡ„зҠ¶жҖҒжңәпјҢSurfaceжҳҜOpenGL ESз»ҳеӣҫзҡ„вҖңз”»еёғвҖқвҖҰвҖҰ
Xilinxе…¬еҸёзҡ„FPGA_FFT_еә”用笔记пјҢиҜҰз»ҶйҖҡдҝ—зҡ„и®Іи§ЈдәҶfftз®—жі•
еҗ„з§Қ笔记
Android_Activityе’ҢIntentжңәеҲ¶еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°
EPLAN_P8_еҹ№и®ӯ笔记.doc
дә‘笔记项зӣ®дё»иҰҒз”ЁдәҺе®ўжҲ·еңЁзәҝеӯҰд№ ж—¶и®°еҪ•з¬”и®°пјҢеңЁиҜҘеҠҹиғҪеҹәзЎҖдёҠеҸҲжү©еұ•дәҶеҲҶдә«пјҢ收и—ҸпјҢжҙ»еҠЁзӯүеҠҹиғҪпјҢиҜҘйЎ№зӣ®йҮҮз”ЁMVCи®ҫи®ЎжЁЎејҸпјҢSpring+MyBatisпјҢAjax,jQueryжЎҶжһ¶ејҖеҸ‘пјҢеңЁжӯӨжҠҖжңҜдёҠе®һзҺ°йЎ№зӣ®зҡ„зҷ»еҪ•жЁЎеқ—пјҢ笔记жң¬жЁЎеқ—пјҢ笔记模еқ—пјҢ...
android service еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°пјҲдёҠгҖҒдёӢпјүandroid service еӯҰд№ з¬”и®°пјҲдёҠгҖҒдёӢпјү
еӯҰд№ javaзҡ„笔记пјҢеҹәдәҺж•ҷиӮІжңәжһ„ж•ҙзҗҶпјҢе…ҚеҺ»еӯҰд№ иҖ…иҠұеҺ»иҝҮеӨҡзҡ„ж—¶й—ҙеңЁжҹҘжүҫиө„ж–ҷдёҠпјҢиҠӮзәҰж—¶й—ҙпјҢй«ҳж•ҲеӯҰд№
Android еҗ„зұ»е®үеҚ“жҺ§д»¶еұһжҖ§иҜҰз»ҶдҪҝз”ЁиҜҙжҳҺпјҢеҝ«йҖҹжҺҢжҸЎandroidе…Ҙй—ЁеҹәзЎҖгҖӮ